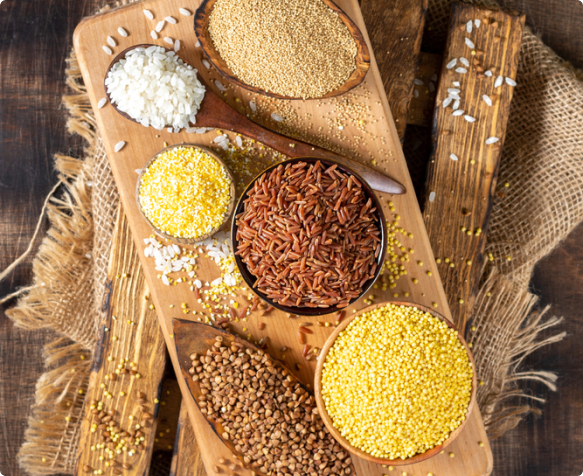
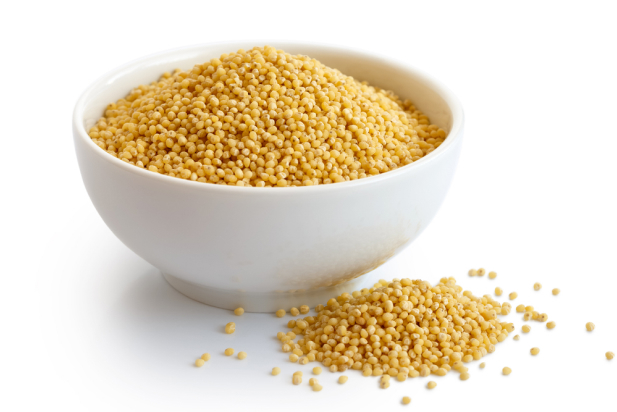
According to the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), millets are classified into Major Millets and Minor Millets based on their grain size. Major millets include sorghum, pearl millet and finger millet. Barnyard, kodo, foxtail, little and proso are the minor millets. There is another class of millets—the pseudo millets—which are nutritionally similar and must be acknowledged as valuable in this context. They are called so because they are not part of the Poaceae botanical family.
Millet Benefits
Inclusion of millets in daily diets adds a multitude of nutritional benefits providing various macro and micronutrients in the diet. They are considered as functional foods, rich in nutritionally essential compounds. Millets have a high vitamin content, including vitamin A, vitamin B, vitamin C.